Information for Teachers
Curriculum links
Australian Science Standards
BS (ACSSU44) Living things can be grouped on basis of observable features and distinguished from non-living things
BS (ACSSU44) Characteristics of living things such as growing, moving, sensitivity and reproducing
SS01.2 All life forms, including human life, are connected through ecosystems on which they depend for their wellbeing
New Zealand Science Achievement Objectives
LW: There are life processes common to all living things and that these occur in different ways
LW: How living things are suited to their particular habitat and how they respond to environmental changes, both natural and human-induced
LW: Groups of living things in our world have changed over long periods of time
Helpful websites
You may want to direct your students to some or all of these websites to help with their investigations.
Acutely endangered mammals:
http://www.allaboutwildlife.com/endangered-species/endangered-species-population-numbers/3596
https://www.fws.gov/endangered/species/us-species.html
No longer endangered:
http://www.toptenz.net/10-animals-no-longer-endangered-species-list.php
http://www.iflscience.com/plants-and-animals/7-animals-saved-near-extinction/
How to search the internet
1 Keep your request short
Fewer words will give a more accurate search.
2 Choose exactly what you want
For example: Arctic Circle Climate
3 Use quotes
Double quotes around a set of words tell the search engine to consider those exact words in that exact order without any change. For example: “Arctic Circle Climate”
4 Use the plus sign (+)
If you add a plus sign (+) between words, the internet will search for all the words. For example: migrate+birds+whales+mammal
5 Use the minus sign (–) to say what you don’t want
Use a minus sign (–) to show words you do not want to appear in your results. For example: if you search for burrowing animals and do not want mammals in your search, –mammals will exclude mammals. Note that you need to put a space before the minus sign for the word to be excluded.
6 Be very clear about what you don’t want
Part 1
Ask questions and make predictions
After reading Going, Going, Gone? you may have many questions about why animals became extinct.
List your questions
- Compare your list with questions that others have.
- Choose a question you would like to investigate.
- You can work alone, with a partner, or in a small group.
You may want to choose one or more of these questions to investigate
Q1. Make a list of the animals that may have once been in danger of becoming extinct, but seem to be doing well today. Why has this happened?
Q2. Which animals are seriously in danger of becoming extinct today? Why? Can anything be done to help them?
Go to Part 2 Plan and investigate →Part 2
Plan and investigate
Do searches in the internet or in books or talk to people who can help to find the information you are looking for.
Your teacher may suggest suitable websites for further information.
Go to Part 3 Record and analyse data →Part 3
Record and analyse data
Find a way of recording your information that will allow you to see any patterns in the data.
Data Chart for acutely endangered animals
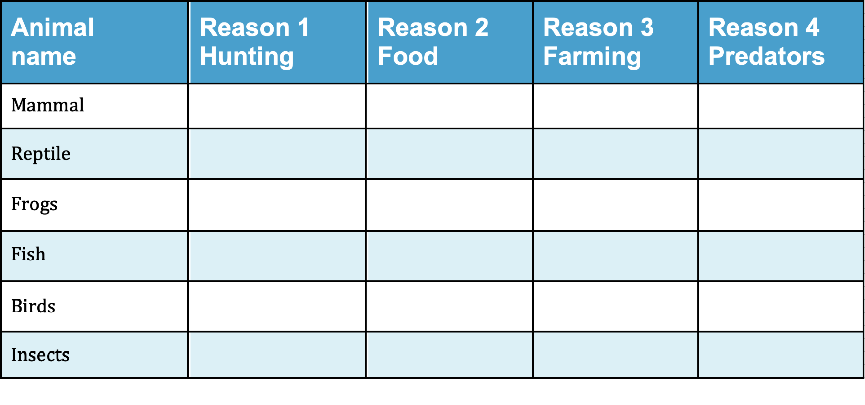 Download Chart
Download Chart
Go to Part 4 Evaluate the information →
Part 4
Evaluate the information
1. Look over the information you have gathered and the patterns you have found.
Why are these animals facing extinction? Can anything be done to help them?
2. Search for other patterns.
Have animals like these been rescued before? How? What might happen if new laws protect them?
3. Makes notes about what you find.
Go to Part 5 Communicate and share ideas →Part 5
Communicate and share ideas
Look over all of the information that you have gathered in your investigation.
What are the most important ideas about projects to protect animals in danger of extinction?
Make a chart showing the most important ideas.
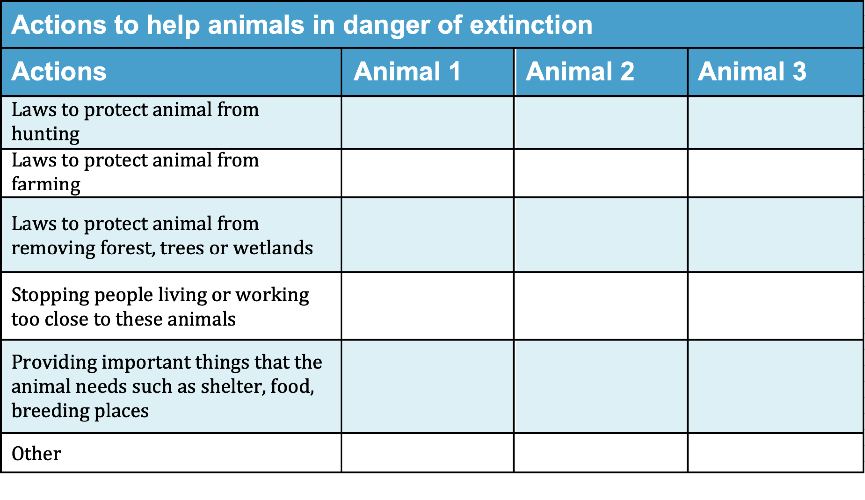 Download Chart
Download Chart
← Return to menu
